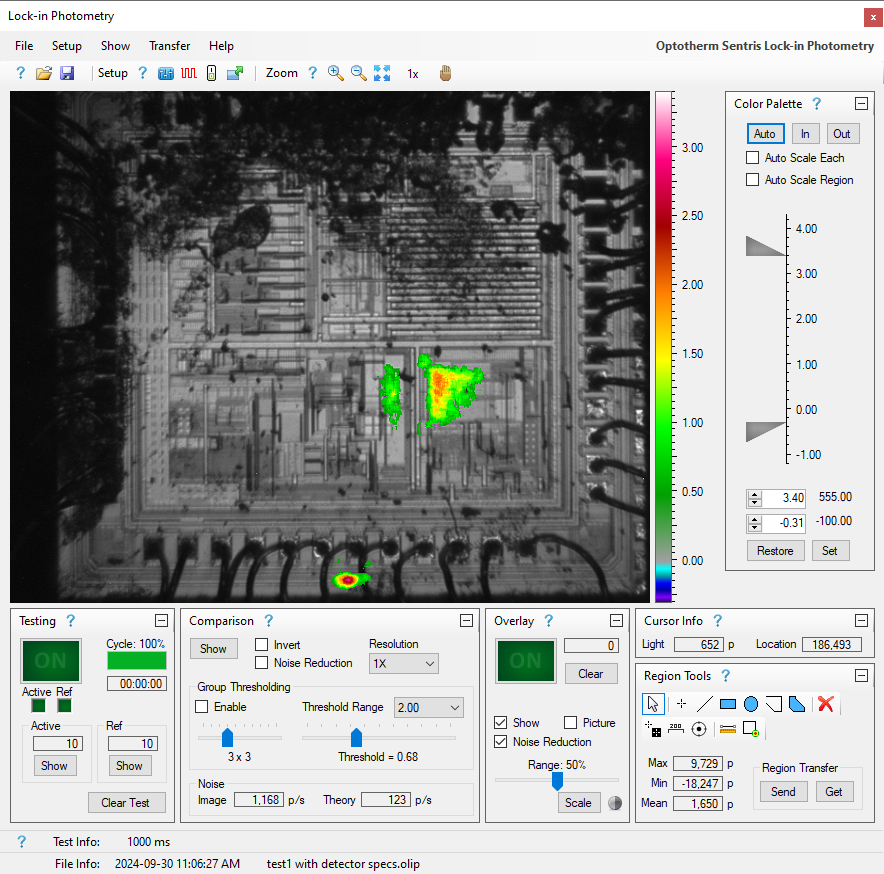
Lock-in Photometry
For use with Thermalyze Thermal Image Analysis Software
PN0896
Lock-in photometry is a tool similar to Emission Microscopy (EMMI) and Photon Emission Microscopy (PEM) and is used to detect and locate faults on semiconductor devices by detecting emitted photons in the short wave infrared (SWIR) region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Applications
A camera sensitive to SWIR energy is used to detect photons with wavelengths between 400 and 1700nm that are emitted by electron-photon recombination caused by faults such as the following:
- P-N junction leakage
- Gate oxide leakage
- Latch-up
- Transistor failure caused by an open or short circuit
Overview
Lock-in Photometry
Lock-in photometry is a test process comparing the emissions of a biased device to the emissions of an optical shutter (or an unbiased device). The following description is oversimplified, but helps to provide a basic understanding of the lock-in process. Over many cycles, captured images of the biased device (Active Images) are added together. Likewise, captured images of the unbiased device (Reference Images) are added together. The unbiased sum is subtracted from the biased sum resulting in a comparison image that represents emission differences between the biased and unbiased state. As the lock-in test continues, more and more images are added, resulting in a comparison image with higher and higher sensitivity. Test sensitivity is inversely proportional to the square root of the number of images captured during a test.
Related Products
Specifications
Operation
Troubleshoot
Maintenance